# 使用 Vue 脚手架
# 1. 初始化脚手架
# 1.1. 说明
Vue 脚手架是 Vue 官方提供的标准化开发工具(开发平台)
最新的版本是 5.x
官网: https://cli.vuejs.org/zh/ (opens new window)
# 1.2. 步骤
1.全局安装 @vue/cli :
# 设置淘宝镜像源
npm config set registry https://registry.npm.taobao.org
# 全局安装
npm install -g @vue/cli
# 查看版本
vue -V
# @vue/cli 5.0.8
2.创建项目:
# 切换到工作空间
vue create vue-proj
3.启动项目:
npm run serve
4.访问 http://localhost:8080/ (opens new window)
# 1.3. webpack 配置
Vue 脚手架隐藏了所有 webpack 相关的配置,
若想查看具体的 webpack 配置,请执行:
vue inspect > webpack-config-output.js
# 1.4. 模板项目结构
vue-proj/
public/
favicon.ico # 页签图标
index.html # 主页面
src/
assets/ # 存放静态资源
logo.png
component/ # 存放组件
HelloWorld.vue
App.vue # 汇总所有组件
main.js # 入口文件
.gitignore # git 版本管制忽略的配置
babel.config.js # babel 的配置文件
package.json # 应用包配置文件
README.md # 应用描述文件
package-lock.json # 包版本控制文件
vue-proj/public/index.html:
<!--
BASE_URL: 指向 public 目录
-->
<link rel="icon" href="<%= BASE_URL %>favicon.ico">
# 2. Vue 文件说明
# 2.1. 引入 Vue
vue-proj/main.js :
// 引入的是哪个文件???
import Vue from 'vue';
# 2.2. 引入的是哪个
查看 node_modules/vue/package.json :
{
"name": "vue",
"version": "2.7.14",
"main": "dist/vue.runtime.common.js",
"module": "dist/vue.runtime.esm.js",
"unpkg": "dist/vue.js",
"jsdelivr": "dist/vue.js",
}
# 2.3. package.json 相关配置
# 2.3.1. npm 包入口配置
| 配置 | 规范 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| module | esm | 现代 ECMA 规范,摇树性能好,首推使用 |
| main | cjs | node 使用的 require 规范,无摇树 |
| browser | umd | 支持 cjs、amd、global(window) ,一般用在浏览器中 |
对 webpack 而言,使用的顺序为: browser -> module -> main
# 2.3.2. CDN 相关配置
| 配置 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| unpkg | npm: unpkg.com/:package@:version/:file |
| jsdelivr | npm: https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/包名@版本号/目录 github: https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/用户名称/仓库名称@版本号/目录 |
# 2.4. vue 文件类型
| 文件名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| vue.js | 完整版,包含 core(核心) 和 compiler(模板编译器) |
| vue.runtime.js | 运行时版本,只有 core |
| 文件名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| vue.js | 完整版,UMD 版 |
| vue.common.js | 完整版,CommonJS 版 |
| vue.esm.js | 完整版,ES 版 |
# 2.5. 总结
开发态:
用 vue-template-compiler 编译 .vue 文件
运行态:
使用 vue.runtime.js
没有模板编译器:
不能使用
options.template配置项需要使用
options.render配置项来渲染模板import App from './App.vue' new Vue({ render: function(createElement) { return createElement(App); } });
使用完整版:
import Vue from 'vue/dist/vue.esm';
package.json 入口配置:
- 不要使用
browser - 优先使用
module module和main同时存在,webpack 优先使用module
# 2.6. 参考
- package.json配置详解,让你一看就会(上) (opens new window)
- 浅谈package.json中main、module、browser字段对webpack的重大影响 (opens new window)
# 3. vue.config.js 配置文件
官网:https://cli.vuejs.org/zh/config/ (opens new window)
导出:vue inspect > output.js 可以导出 webpack 配置项
常用配置:
| 配置 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| lintOnSave | 每次保存时 lint 代码,true 或 'warning' 不会导致编译失败 |
| pages | 多页面配置 |
# 4. ref 属性
作用: 给元素或子组件注册引用
使用:
<template>
<!-- 普通 HTML 元素 -->
<div ref='elt'></div>
<!-- 组件 -->
<Person ref='cp' />
</template>
<script>
export default {
mounted() {
this.$refs.elt; // 返回 DOM 元素(HTMLElement 的实例)
this.$refs.cp; // 返回 vc(VueComponent 的实例,Person 的实例)
}
}
</script>
# 5. props 属性
功能:让组件接收外部传过来的数据
传数据:(父组件)
<!-- 如果不用 v-bind,则传入的都是字符串 -->
<Demo name="张三" :gender="'男'" :age="18" />
接数据:(子组件)
// 只接收
options = {
props: [ 'name', 'gender', 'age' ]
}
// 限制类型
options = {
props: {
name: String,
gender: String,
age: Number,
}
}
// 限制类型、限制必要性、指定默认值
options = {
props: {
name: {
type: String,
required: true,
},
gender: {
type: String
},
age: {
type: Number,
default: 18
},
}
}
备注:
- props 是只读的,Vue 底层会监测你对 props 的修改,如果进行了修改,就会发出警告
如果要修改,则拷贝到 data 中进行修改
options = { props: [ 'age' ], // Vue 先接收 props 再处理 data(),所以 data() 中可以读取到 props // 如果 data() 与 props 有属性冲突,则以 props 的优先 data() { return { newAge: this.age, }, }, }
# 6. mixin(混入)
功能:可以把多个组件共用的配置提取成一个混入对象
定义:
export default {
data(){ return { /* ... */ }; },
methods:{ /* ... */ },
created() { /* ... */ },
mounted() { /* ... */ },
}
使用:
import myMixin from '...';
// 全局混入,所有的 vc、vm 都有效
Vue.mixin(myMixin);
// 局部混入,当前组件有效
options = {
mixins: [ myMixin ],
};
注意:
- 当配置冲突时,生命周期函数都会执行,非生命周期配置以当前组件优先。
# 7. 插件
功能:用于增强 Vue
本质:
- 包含 install 方法的一个对象
- install 的第一个参数是 Vue,第二个以后的参数是插件使用者传递的数据。
定义:
export default {
install(Vue, options) {
// 1. 添加全局过滤器
Vue.filter(/* .... */)
// 2. 添加全局指令
Vue.directive(/* .... */)
// 3. 配置全局混入(合)
Vue.mixin(/* .... */)
// 4. 配置全局组件
Vue.component(/* ... */);
// 5. 添加实例方法
Vue.prototype.$myMethod = function () {/* ... */}
Vue.prototype.$myProperty = xxxx
}
};
使用:
Vue.use(myPlugin);
Vue.use(myPlugin, { prop1: value1, prop2: value2 });
# 8. scoped 样式
功能:让样式在局部生效(只在当前组件生效),防止冲突。
使用:
<template>
<div class="demo">123</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
.demo { color: red; }
</style>
解析后:
<div class="demo" data-v-123456>123</div>
<style>
.demo[data-v-123456]{ color: red; }
</style>
其他:
- 可以通过
<style lang="less">指定使用 less 语法写样式
# 9. TodoList
# 9.1. 父子传值
父组件把 数据和操作数据的方法 传给子组件。
<!-- App.vue -->
<template>
<div>
<Child :items="items" :addItem="addItem" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
items: [1, 2, 3]
}
},
methods: {
addItem(item) {
this.items.unshift(item);
}
}
};
</script>
<!-- Child.vue -->
<template>
<div>
<div v-for="item in items">{{ item }}</div>
<button @click="add">add</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: [ 'items', 'addItem' ],
methods: {
add() {
this.addItem(Math.floor(Math.random() * 10));
}
}
}
</script>
# 9.2. 不要修改 props 里的属性
<template>
<div>
<!-- 不要对 props 里的属性使用 v-model -->
<input type="checkbox" v-model="person.isStudent" />
{{ age }}
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: [
'person', // { name: '韩梅梅', isStudent: true }
'age',
],
mounted() {
this.age = 18; // Vue 会报错
this.person = {}; // Vue 会报错
this.person.age = 19; // Vue 不会报错
},
};
</script>
# 9.3. 总结
# 9.3.1. 组件化编码流程
拆分静态组件:组件要按照功能点拆分,命名不要与 HTML 元素冲突。
实现动态组件:考虑好数据的存放位置,数据是一个组件在用,还是一些组件在用:
- 一个组件在用:放在组件自身即可。
- 一些组件在用:放在他们共同的父组件上(状态提升)。
实现交互:从绑定事件开始。
# 9.3.2. props适用于
- 父组件 ==> 子组件 通信
- 子组件 ==> 父组件 通信(要求父先给子一个函数)
# 9.3.3. 使用 v-model 时要切记
v-model 绑定的值不能是 props 传过来的值,因为 props 是不可以修改的!
props 传过来的若是对象类型的值,修改对象中的属性时 Vue 不会报错,但不推荐这样做。
# 10. webStorage
存储内容大小一般支持 5MB 左右(不同浏览器可能还不一样)
浏览器端通过 window.sessionStorage 和 window.localStorage 属性来实现本地存储机制。
相关API:
| API | 说明 |
|---|---|
xxxxxStorage.setItem('key', 'value') | 该方法接受一个键和值作为参数,会把键值对添加到存储中, 如果键名存在,则更新其对应的值。 |
xxxxxStorage.getItem('person'); | 该方法接受一个键名作为参数,返回键名对应的值。 |
xxxxxStorage.removeItem('key'); | 该方法接受一个键名作为参数,并把该键名从存储中删除。 |
xxxxxStorage.clear() | 该方法会清空存储中的所有数据。 |
备注:
- sessionStorage 存储的内容会随着浏览器窗口关闭而消失。
- localStorage 存储的内容,需要手动清除才会消失。
xxxxxStorage.getItem(xxx)如果xxx对应的value获取不到,那么getItem的返回值是null。JSON.parse(null)的结果依然是null。
# 11. 组件的自定义事件
# 11.1. 作用
一种组件间通信的方式,适用于:子组件 ===> 父组件
# 11.2. 使用场景
子想给父传数据,那么就要在父中给子绑定自定义事件(事件的回调在父中)。
# 11.3. 绑定自定义事件
第一种方式,在父组件中:
<Demo @myEvent="test"/>
<!-- 或者 -->
<Demo v-on:myEvent="test"/>
第二种方式,在父组件中:
<Demo ref="demo"/>
<script>
data = {
mounted(){
this.$refs.xxx.$on('myEvent',this.test)
},
methods: {
test(arg1, arg2, ...) {
/* ... */
},
}
}
</script>
备注:
- 若想让自定义事件只能触发一次,可以使用
once修饰符,或$once方法。
# 11.4. 触发自定义事件
this.$emit('myEvent', data1, data2, ...)
# 11.5. 解绑自定义事件
// 单个
this.$off('myEvent');
// 多个
this.$off(['myEvent', 'myEvent2']);
// 所有
this.$off();
# 11.6. 绑定原生事件
组件上也可以绑定原生 DOM 事件,需要使用 native 修饰符。
# 11.7. 注意
通过 this.$refs.xxx.$on('myEvent',回调) 绑定自定义事件时,
回调要么配置在 methods 中,要么用箭头函数,否则 this 指向会出问题!
# 11.8. 示例
<!-- App.vue -->
<template>
<Child @success="handleChild1" />
<Child ref="child2" />
<!-- 给组件绑定事件,默认都是自定义事件;通过 native 修饰符绑定原生事件 -->
<Child @click.native="handleClick" />
</template>
<script>
export default {
mounted() {
this.$refs.child2.$on('success', this.handleChild2);
this.$refs.child2.$on('success', function() {
// this 的指向为 child2 vc
});
},
methods: {
handleChild1(arg1, arg2, ...args) {
console.log(arg1, arg2, args)
},
handleChild2(arg1, arg2, ...args) {
console.log(arg1, arg2, args)
},
},
}
</script>
<!-- Child.vue -->
<template>
<div><button @click="handleClick">click</button></div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
handleClick() {
this.$emit('success', 'I make it!', '哈哈哈', '哦也');
},
unbind() {
this.$off('event1'); // 单个
this.$off(['event1', 'event2']); // 多个
this.$off(); // 所有
},
}
}
</script>
# 12. 全局事件总线(GlobalEventBus)
# 12.1. 作用
一种组件间通信的方式,适用于 任意组件间通信。
# 12.2. 安装全局事件总线
// root
new Vue({
beforeCreate() {
// 安装全局事件总线,$bus 就是当前应用的 vm
Vue.prototype.$bus = this
},
})
# 12.3. 使用事件总线
接收数据:谁收谁监听
options = {
methods: {
demo(data){ /* ... */ }
},
mounted() {
this.$bus.$on('myEvent',this.demo);
},
beforeDestroy() {
this.$bus.$off('myEvent');
}
}
提供数据:谁发谁触发。
this.$bus.$emit('myEvent', data1, data2, ...);
# 12.4. 注意
最好在 beforeDestroy 钩子中,用 $off 去解绑当前组件所用到的事件。
# 13. 消息订阅与发布(pubsub)
# 13.1. 作用
一种组件间通信的方式,适用于 任意组件间通信。
# 13.2. 安装
npm i pubsub-js
# 13.3. 引入
import pubsub from 'pubsub-js'
# 13.4. 使用
接收数据:谁收谁订阅。
options = {
methods: {
demo(msgName, data){ /* ... */ }
},
mounted() {
this.pid = pubsub.subscribe('myMsg',this.demo) // 订阅消息
},
beforeDestroy() {
pubsub.unsubscribe(this.pid);// 取消订阅
},
};
提供数据:谁发谁发布。
pubsub.publish('myMsg', data) // 发布消息
# 13.5. 注意
最好在 beforeDestroy 钩子中,用 pubsub.unsubscribe(pid) 去取消订阅。
消息的发送与订阅,难以跟踪到,不利于调试。
# 14. nextTick
语法:
this.$nextTick(回调函数)
作用:在下一次 DOM 更新结束后执行其指定的回调。(本次:改了数据,未更新DOM。下次:更新DOM。)
什么时候用:当改变数据后,要基于更新后的新 DOM 进行某些操作时,要在 nextTick 所指定的回调函数中执行。
# 15. 过渡与动画
# 15.1. 动画效果
通过 @keyframes 、animation 自定义动画来实现
<transition appear>
<h1 v-show="visible">我是张三</h1>
</transition>
<style scoped>
/* 进入就激活 */
.v-enter-active {
animation: my-animation 1s;
}
/* 离开就激活 */
.v-leave-active {
animation: my-animation 1s reverse; /* 倒着播放 */
}
@keyframes my-animation {
from {
transform: translateX(-100%);
}
to {
transform: translateX(0);
}
}
</style>
# 15.2. 过渡效果
通过 transition 来实现
<transition appear>
<h1 v-show="visible">我是张三</h1>
</transition>
<style scoped>
/* 进入的起点 */
.v-enter {
transform: translateX(-100%);
}
/* 进入就激活 */
.v-enter-active {
transition: 1s linear;
}
/* 进入的终点 */
.v-enter-to {
transform: translateX(0);
}
/* 离开的起点 */
.v-leave {
transform: translateX(0);
}
/* 离开就激活 */
.v-leave-active {
transition: 1s linear;
}
/* 离开的终点 */
.v-leave-to {
transform: translateX(-100%);
}
</style>
# 15.3. 多个元素过渡
多个元素:
- 要么使用
v-ifv-else-ifv-else,最终只显示一个元素 - 要么使用
<transition-group>
<transition appear>
<h1 v-if="visible">我是张三</h1>
<h1 v-else>我是李四</h1>
</transition>
<transition-group appear>
<h1 v-show="visible" key="1">我是张三</h1>
<h1 v-show="!visible" key="2">我是李四</h1>
</transition-group>
# 15.4. 集成第三方动画
安装:
npm install animate.css
引入:
import 'animate.css';
选择动画效果: https://animate.style/ (opens new window)
配置:
<!--
name="animate__animated xxx"
元素会添加上 animate__animated 类名,
xxx 为真正的前缀,即 xxx-enter, xxx-enter-active, ...
-->
<transition-group
appear
enter-active-class="animate__animated animate__swing"
leave-active-class="animate__animated animate__backOutUp"
>
<h1 v-show="visible" key="1">我是张三</h1>
<h1 v-show="!visible" key="2">我是李四</h1>
</transition-group>
# 15.5. 总结
作用:在插入、更新或移除 DOM元素时,在合适的时候给元素添加样式类名。
图示:
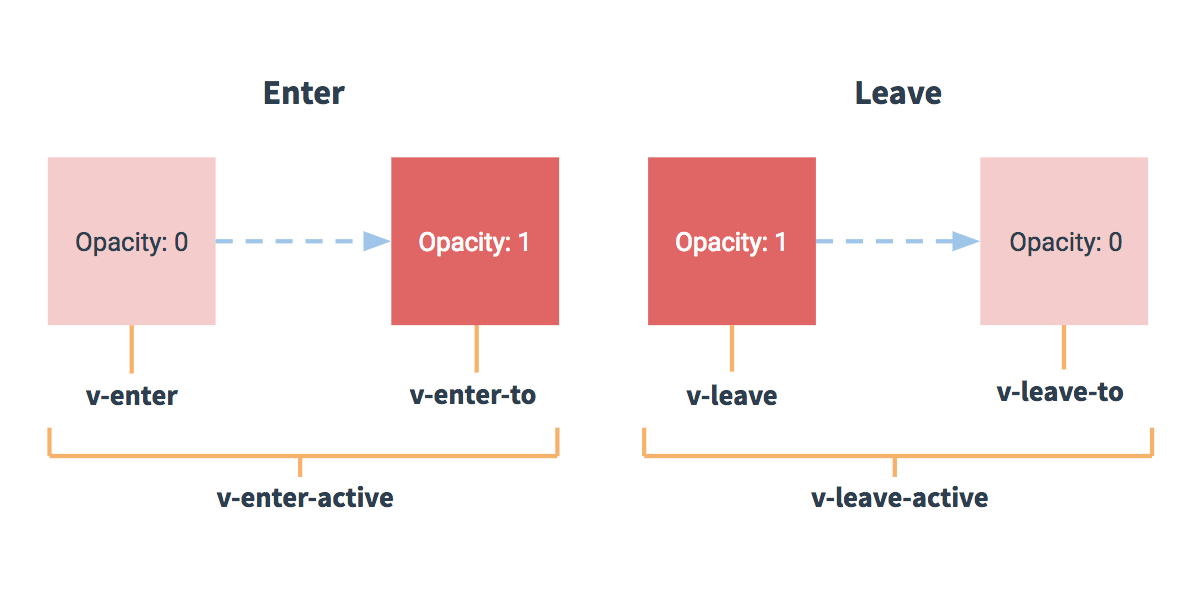
写法:
准备好样式:
- 元素进入的样式:
v-enter:进入的起点v-enter-active:进入过程中v-enter-to:进入的终点
- 元素离开的样式:
v-leave:离开的起点v-leave-active:离开过程中v-leave-to:离开的终点
- 元素进入的样式:
使用
<transition>包裹要过度的元素,并配置name属性:<transition name="hello"> <h1 v-show="visible">你好啊!</h1> </transition>备注:若有多个元素需要过度,则需要使用:
<transition-group>,且每个元素都要指定key值。
上一篇: 下一篇:
